Safety First on the Pour Site: Equipment, PPE & Culture in Concrete Work
The construction industry’s commitment to worker safety has reached unprecedented levels of sophistication, with concrete construction safety leading the transformation through innovative personal protective equipment, advanced site equipment, and comprehensive safety culture initiatives. As high-intensity concrete operations present unique hazards ranging from chemical exposure to physical injuries, the evolution of safety technologies and management approaches is creating work environments that protect personnel while maintaining productivity and quality standards.
The Critical Importance of Concrete Construction Safety
Concrete construction operations present a complex array of safety challenges that require specialized approaches and equipment. The combination of heavy machinery, chemical exposure, physical demands, and time-sensitive operations creates environments where traditional safety measures often prove inadequate. Statistics indicate that construction workers face injury rates significantly higher than other industries, making advanced safety systems essential for protecting personnel and maintaining project viability.
The economic implications of construction accidents extend far beyond immediate medical costs to encompass project delays, insurance claims, regulatory penalties, and long-term liability exposure. Comprehensive concrete construction safety programs that prevent incidents deliver substantial returns on investment while protecting the most valuable resource on any project: the workforce.
Modern safety expectations have evolved beyond basic compliance to encompass proactive hazard identification, predictive risk management, and continuous improvement approaches that create positive safety cultures. These advanced approaches recognize that effective safety systems must integrate seamlessly with construction operations to achieve sustained success.
Revolutionary Personal Protective Equipment Innovations
Smart PPE Technologies

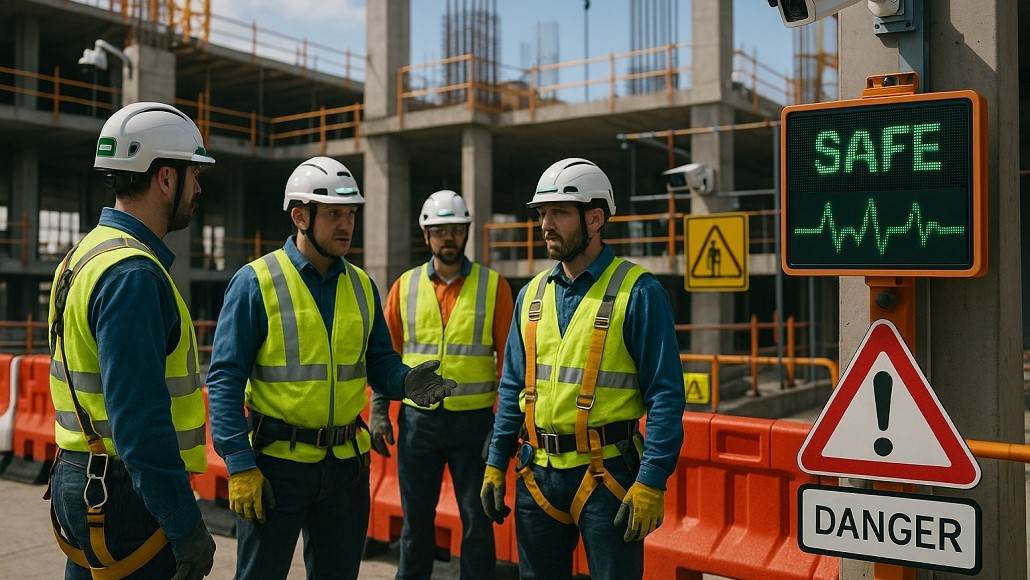
The integration of advanced technologies into personal protective equipment represents one of the most significant developments in concrete construction safety. Smart helmets now incorporate built-in communication systems, environmental sensors, and augmented reality displays that provide real-time safety information and hazard alerts directly to workers.
These intelligent helmets can monitor air quality, detect impact forces, and track worker location while providing two-way communication capabilities that ensure immediate response to emergency situations. Advanced models include heads-up displays that present safety information, project drawings, and hazard warnings without requiring workers to divert attention from their tasks.
Smart safety vests incorporate sensors that monitor vital signs including heart rate, body temperature, and fatigue indicators. These systems provide early warning of heat stress, exhaustion, and other health conditions that could lead to accidents or injuries. Real-time monitoring enables supervisory personnel to intervene before conditions become dangerous.
Advanced Material Technologies
Modern PPE utilizes advanced materials that provide superior protection while improving comfort and usability. Impact-resistant composite materials in helmets offer enhanced protection against falling objects while reducing weight and improving balance. Advanced fabric technologies provide chemical resistance while maintaining breathability that prevents overheating during strenuous activities.
Cut-resistant gloves now achieve exceptional protection levels while maintaining dexterity required for precision work. These materials enable workers to handle reinforcing steel, formwork, and tools safely without compromising their ability to perform detailed tasks effectively.
Respiratory protection systems have evolved to provide enhanced filtration capabilities while reducing breathing resistance. Advanced filter media remove both particulate matter and chemical vapors while maintaining comfort during extended use periods.
Ergonomic Design Integration
Contemporary PPE design prioritizes ergonomic considerations that encourage consistent use while reducing physical strain. Properly fitted equipment reduces fatigue and discomfort that traditionally discouraged workers from maintaining protection throughout their shifts.
Adjustable suspension systems in hard hats ensure proper fit across diverse head sizes and shapes while providing impact absorption that exceeds traditional designs. Lightweight materials and improved weight distribution reduce neck strain during extended wear periods.
Safety footwear now incorporates advanced sole designs that provide slip resistance on wet concrete surfaces while offering puncture protection and electrical hazard protection. Comfortable insoles and breathable materials improve wearability during long work shifts.
Advanced Site Equipment and Safety Systems
Automated Safety Monitoring
Construction sites now utilize automated monitoring systems that continuously assess environmental conditions and worker safety compliance. AI-powered camera systems can identify workers not wearing required PPE, unsafe behaviors, and hazardous conditions without human supervision.
Environmental monitoring systems track air quality, noise levels, and dust concentrations to ensure compliance with occupational health standards. Real-time alerts enable immediate response when conditions exceed safe limits, protecting workers from exposure to hazardous substances.
Fall detection systems utilize wearable sensors and fixed monitoring equipment to identify falls immediately and summon emergency response. These systems can differentiate between normal work activities and actual emergencies, reducing false alarms while ensuring rapid response to genuine incidents.
Equipment Safety Integration
Modern concrete construction equipment incorporates advanced safety systems that protect operators and nearby workers. Proximity sensors prevent equipment operation when personnel are detected in danger zones, while backup alarms and visual warning systems enhance awareness of equipment movement.
Automated shutdown systems can halt equipment operation when unsafe conditions are detected, including excessive vibration, overheating, or loss of hydraulic pressure. These systems prevent equipment failures that could result in injuries while protecting valuable machinery investments.
Remote control capabilities enable operators to maintain safe distances from hazardous operations including demolition, excavation in unstable areas, and work near overhead hazards. These technologies reduce operator exposure while maintaining operational efficiency.
Building Positive Safety Culture
Leadership and Accountability
Effective concrete construction safety depends on strong leadership commitment that prioritizes worker protection above short-term productivity pressures. Safety-focused leadership creates organizational cultures where workers feel empowered to report hazards, suggest improvements, and halt work when unsafe conditions are identified.
Accountability systems ensure that safety responsibilities are clearly defined and consistently enforced at all organizational levels. Regular safety performance reviews and recognition programs reinforce positive behaviors while identifying areas for improvement.
The integration of safety metrics into project performance measurement ensures that safety considerations receive equal priority with schedule and cost objectives. This balanced approach prevents safety compromises that could result in accidents and long-term project impacts.
Training and Education Programs
Comprehensive training programs ensure that workers understand hazards specific to concrete construction and possess the knowledge necessary to work safely. Interactive training methods including virtual reality simulations provide realistic hazard exposure without actual risk, enabling workers to practice emergency responses and safe work procedures.
Ongoing education programs keep workers current with evolving safety requirements, new equipment technologies, and lessons learned from industry incidents. Regular refresher training reinforces critical safety concepts while introducing new technologies and procedures.
Mentorship programs pair experienced workers with newcomers to provide practical safety guidance and reinforce positive safety behaviors. These relationships create supportive environments where safety knowledge transfers effectively between generations of workers.
Communication and Feedback Systems
Effective safety cultures depend on open communication channels that enable workers to report hazards, suggest improvements, and receive feedback on safety performance. Regular safety meetings provide forums for discussing site-specific hazards, sharing lessons learned, and recognizing positive safety behaviors.
Digital communication platforms enable real-time reporting of safety concerns and immediate response to emerging hazards. Mobile applications allow workers to photograph hazards, report near-miss incidents, and access safety resources from their personal devices.
Feedback systems ensure that worker suggestions receive prompt attention and appropriate action. This responsiveness demonstrates management commitment to safety while encouraging continued participation in safety improvement initiatives.
Specialized Safety Protocols for Concrete Operations
Chemical Exposure Protection
Concrete construction involves exposure to alkaline materials, chemical admixtures, and curing compounds that can cause skin irritation, respiratory problems, and chemical burns. Specialized protocols address these exposures through appropriate PPE selection, work procedures, and emergency response planning.
Skin protection protocols emphasize the importance of chemical-resistant gloves, protective clothing, and immediate washing facilities. These measures prevent cement burns and dermatitis that can result from prolonged skin contact with fresh concrete.
Respiratory protection programs address dust exposure during cutting, grinding, and demolition operations. These programs include hazard assessment, respirator selection, fit testing, and maintenance procedures that ensure effective protection against silica dust and other airborne contaminants.
Physical Safety Considerations
The physical demands of concrete construction require specialized safety approaches that address lifting, repetitive motions, and ergonomic stresses. Back injury prevention programs provide training in proper lifting techniques while emphasizing the use of mechanical lifting aids when possible.
Heat stress prevention becomes critical during concrete placement operations that may continue for extended periods regardless of weather conditions. These protocols include hydration programs, cooling systems, work-rest cycles, and heat illness recognition training.
Struck-by hazards from equipment, falling objects, and structural collapses require comprehensive hazard identification and control measures. These include proper traffic control procedures, overhead protection systems, and communication protocols between equipment operators and ground personnel.
Technology Integration and Future Developments
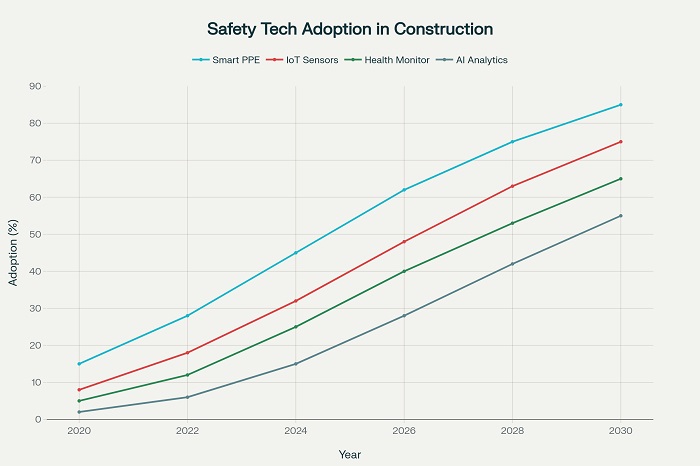
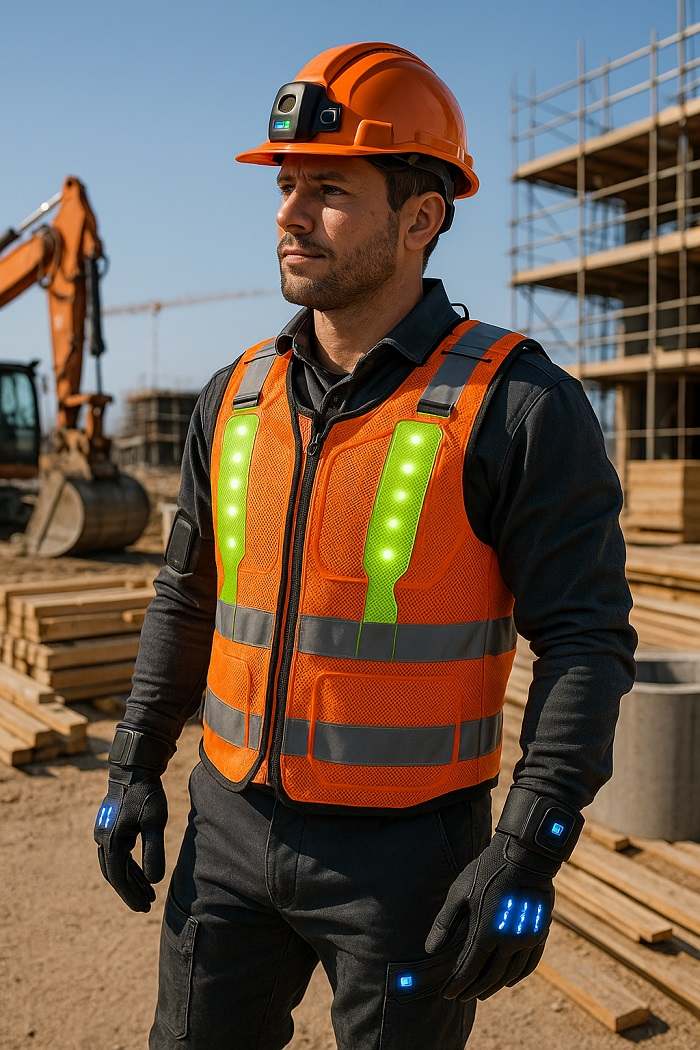
Wearable Technology Advancement
Emerging wearable technologies promise to further enhance concrete construction safety through more sophisticated monitoring and intervention capabilities. Future devices will integrate multiple sensor types to provide comprehensive health and safety monitoring while maintaining comfort and usability.
Exoskeleton technologies are entering construction applications to reduce physical strain and prevent musculoskeletal injuries. These devices augment worker strength and endurance while providing back support during lifting and repetitive tasks.
Predictive Safety Analytics
Artificial intelligence applications will enable predictive safety analytics that identify potential accident scenarios before they occur. These systems will analyze patterns from multiple data sources including weather conditions, worker behavior, equipment performance, and historical incident data to forecast safety risks.
Machine learning algorithms will continuously improve risk assessment capabilities by learning from new data and incident reports. These systems will enable proactive safety interventions that prevent accidents rather than responding to them after they occur.
Integrated Safety Ecosystems
Future safety systems will integrate multiple technologies into comprehensive ecosystems that provide seamless protection throughout construction operations. These systems will coordinate PPE monitoring, environmental sensors, equipment safety systems, and emergency response protocols to create unified safety management platforms.
The integration of safety systems with project management platforms will enable real-time safety performance tracking and continuous improvement initiatives. These capabilities will support evidence-based safety decisions while demonstrating the value of safety investments to project stakeholders.
The evolution of concrete construction safety represents a fundamental transformation in how the construction industry approaches worker protection and risk management. As these technologies and approaches continue to develop and integrate, they create work environments that protect personnel while enabling the productivity and quality required for successful project completion. This advancement ensures that construction careers can be both rewarding and safe while supporting the industry’s continued growth and development in an increasingly complex and demanding market environment.































