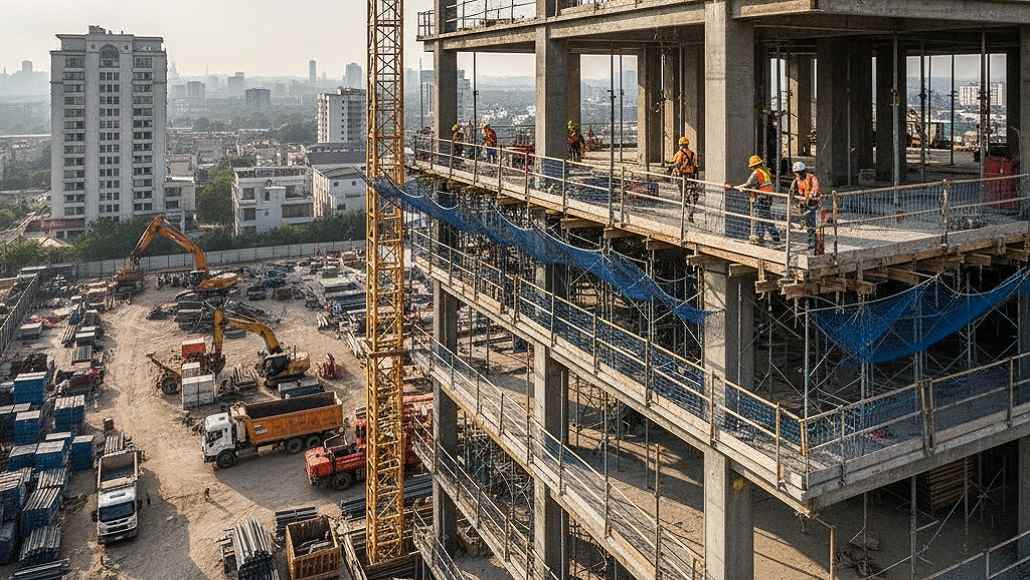
Height Safety Standards and Technologies Construction
Working at height remains the single most dangerous activity in construction, consistently accounting for the largest proportion of fatal accidents across global construction industries. Falls from elevation caused by inadequate protection, equipment failure, or procedural lapses result in devastating consequences for workers, families, and organizations. The evolution of height safety standards construction reflects growing recognition that protecting workers requires comprehensive approaches integrating regulatory frameworks, advanced equipment technologies, rigorous training programs, and organizational safety cultures that prioritize prevention over reaction.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance Requirements
Height safety regulations establish minimum standards that employers must satisfy when construction activities involve potential fall hazards. The Working at Height Regulations applicable in the United Kingdom define working at height as any situation where personnel could fall distances liable to cause injury if precautions were not implemented. This definition encompasses obvious scenarios such as scaffold work and roof access, but extends to less apparent situations including working near excavations or openings where falls to lower levels might occur.
Regulatory frameworks emphasize hierarchy of controls requiring employers to avoid work at height wherever reasonably practicable. When tasks can be accomplished from ground level through alternative methods or equipment, these approaches must be implemented preferentially. Only when elimination proves impractical should organizations proceed to implementing protective measures minimizing fall risks and potential fall consequences.
Planning requirements mandate that work at height must be properly organized with appropriate supervision and control measures. Organizations must conduct thorough risk assessments identifying fall hazards, evaluating injury potential, and determining necessary precautions. These assessments must consider environmental conditions including weather patterns, proximity to fragile surfaces, and presence of overhead hazards. Equipment selection must account for task requirements, site conditions, and worker capabilities ensuring appropriate protection provisions.
Competence requirements extend throughout organizational hierarchies. Persons planning work at height activities must possess sufficient knowledge and experience to identify hazards and specify appropriate controls. Supervisors must understand safety requirements thoroughly enough to verify implementation and address deficiencies. Workers must receive training enabling them to recognize risks, utilize equipment correctly, and respond appropriately to changing conditions. Regular competence verification ensures that capabilities remain current as regulations evolve and technologies advance.
Personal Fall Protection Equipment Evolution
Personal protective equipment for fall protection has undergone remarkable evolution driven by technological advancement and improved understanding of fall dynamics. Modern full-body harnesses distribute arrest forces across shoulders, chest, back, and legs, dramatically reducing injury severity compared to obsolete body belts that concentrated forces on abdominal regions. Harness designs incorporate padding, adjustable sizing, and quick-connect fasteners enhancing comfort and encouraging consistent use.
Energy absorption technologies represent critical innovations addressing the physics of fall arrest. When falls occur, deceleration forces can reach dangerous levels if arrest happens too abruptly. Modern energy absorbing lanyards incorporate tear-away stitching or specially designed materials that progressively fail during fall arrest events, extending stopping distances and reducing peak forces experienced by workers. These devices limit forces to levels that human bodies can withstand, typically around six kilonewtons, even when arresting falls from maximum allowable distances.
Self-retracting lifelines have gained popularity for applications requiring frequent position changes or extended operational durations. These devices automatically maintain appropriate slack while workers move, then lock rapidly when sudden downward acceleration indicates fall occurrence. Advanced models incorporate centrifugal braking systems that engage smoothly, minimizing shock loads while providing reliable fall arrest. Some implementations include integral energy absorbers providing additional deceleration distance when falls approach maximum allowable extents.
Anchorage systems provide critical connection points between workers and building structures. Permanent anchorages installed during construction provide reliable attachment locations for subsequent maintenance and inspection activities. Temporary anchorages must be carefully evaluated ensuring adequate strength for intended applications. Modern height safety standards construction typically require anchorages capable of supporting forces of twenty-two kilonewtons or five thousand pounds, providing substantial safety margins above actual arrest forces.
Fall restraint systems prevent falls from occurring by limiting worker movement to safe zones. These approaches utilize shorter lanyards or retractable devices configured so workers cannot reach edges or openings where falls might occur. Restraint systems eliminate fall arrest force concerns because falls never develop, though proper configuration requires careful measurement and verification ensuring protection effectiveness.
Collective Protection Systems and Equipment
Guardrail systems provide collective protection benefiting all workers in protected areas without requiring individual equipment or training. Properly designed guardrails incorporate top rails at appropriate heights, mid-rails preventing workers from sliding under top rails, and toe boards preventing tools and materials from falling to lower levels. Modern guardrail systems utilize lightweight materials and modular designs enabling rapid installation and reconfiguration as work progresses.
Scaffolding represents the traditional collective protection approach for extensive work at height. Contemporary scaffolding systems incorporate enhanced safety features including integrated guardrails, non-slip platform surfaces, and standardized components ensuring structural adequacy. Mobile scaffolding towers provide flexibility for tasks requiring frequent position changes, incorporating locking mechanisms preventing movement during use and outriggers enhancing stability. Advanced guard rail systems enable scaffolds to be built from the platform level downward, eliminating exposure to fall hazards during assembly.
Mobile elevated work platforms, commonly termed scissor lifts or boom lifts, provide protected working environments at height. These machines incorporate guardrails, non-slip platform surfaces, and emergency descent capabilities. Modern units feature sophisticated control systems preventing tipping, automatic leveling maintaining platform stability on uneven surfaces, and proximity detection alerting operators to nearby obstacles. Despite these protections, fall protection equipment remains required in most jurisdictions recognizing that workers can still be ejected from platforms during certain incident scenarios.
Safety nets provide passive protection capturing workers who fall, distributing impact forces across wide areas minimizing injury severity. Net systems prove particularly valuable during structural steel erection and similar activities where individual fall protection proves impractical. Installation requires careful attention to positioning, ensuring adequate clearance below nets and sufficient upward extension protecting workers throughout their movement ranges. Regular inspection identifies damage requiring repair before nets can provide reliable protection.
Training and Competence Development
Effective height safety training extends beyond basic equipment operation to encompass comprehensive understanding of fall hazards, protection systems, and emergency response procedures. Workers must learn to identify situations requiring fall protection, select appropriate equipment for specific applications, and inspect equipment identifying defects that might compromise protection. Training should address proper harness fitting, anchor point selection, and connection procedures ensuring reliable protection.
Practical demonstrations and hands-on exercises prove essential for competence development. Theoretical knowledge alone proves insufficient; workers must physically practice donning harnesses, connecting to anchorages, and positioning themselves safely. Simulated emergency scenarios enable workers to experience suspension in harnesses, understanding sensations and limitations while practicing rescue procedures in controlled environments. This experiential learning builds confidence and muscle memory critical during actual emergencies.
Rescue planning and emergency response training address scenarios where workers become suspended following fall arrests. Suspension trauma can develop rapidly as harness straps restrict blood circulation, creating medical emergencies within minutes. Workers must understand these risks and know how to summon assistance immediately. Designated rescue personnel require specialized training enabling safe victim recovery from various suspension scenarios. Organizations must maintain rescue equipment in readily accessible locations and conduct regular drills verifying emergency response effectiveness.
Competence verification ensures training effectiveness and identifies refresher needs. Practical assessments observe workers performing actual tasks, evaluating whether they apply learned principles correctly. Written evaluations test knowledge retention and understanding of underlying safety concepts. Regular retraining addresses new equipment technologies, updated regulations, and lessons learned from incidents. Comprehensive training records document competence verification supporting regulatory compliance and organizational due diligence.
Advanced Technologies Enhancing Protection
Wearable technologies are emerging as powerful tools enhancing height safety through real-time monitoring and intervention capabilities. Smart harnesses incorporate sensors detecting falls immediately, automatically alerting supervisors and emergency responders. Some implementations include GPS positioning enabling rapid victim location. Vital sign monitoring capabilities can detect physiological stress indicating suspension trauma development, prioritizing rescue response.
Environmental monitoring systems track wind speeds, temperature extremes, and precipitation that might create unsafe working conditions. Automated alerts notify supervisors when conditions exceed safe thresholds, enabling proactive work suspension before hazardous exposure occurs. Integration with permit-to-work systems can prevent activity authorization under unsuitable conditions.
Augmented reality applications provide workers with visual guidance overlaying critical safety information onto their field of view. These systems can highlight anchor points, display clearance distances, and present real-time warnings about approaching hazards. Training applications utilizing augmented reality enable realistic scenario-based learning without actual height exposure.
Future Directions and Industry Impact
The advancement of height safety standards construction reflects construction industry commitment to protecting workers from fall hazards that have claimed too many lives. Regulatory frameworks establish comprehensive requirements, technological innovations provide enhanced protection equipment, and organizational focus on training and culture creates environments where safety receives appropriate priority.
Integration of artificial intelligence with height safety systems promises further improvements. Machine learning algorithms can analyze patterns in near-miss incidents, identifying precursor conditions that indicate elevated risk. Predictive analytics might enable proactive interventions preventing dangerous situations from developing. Automated compliance monitoring could verify that safety procedures are followed consistently, identifying deviations requiring corrective action.
While working at height will always involve inherent risks, modern approaches substantially reduce these dangers, enabling construction projects to proceed with acceptable safety levels. Continued evolution of standards, technologies, and practices will further enhance worker protection, demonstrating that construction industry commitment to safety translates into measurable improvements in worker outcomes.

































