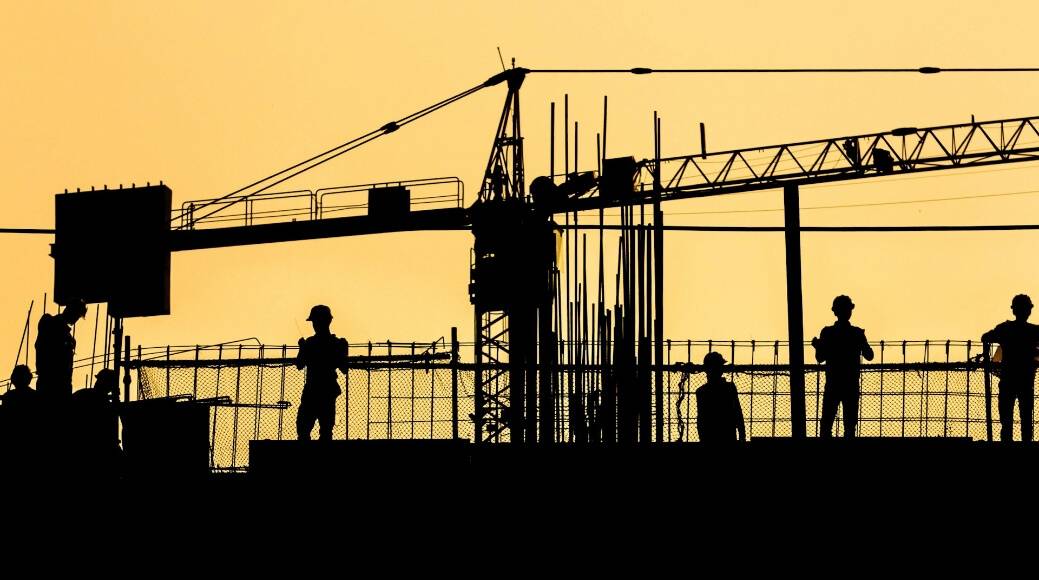
Every job site needs dependable power to function safely and efficiently. Consistent electricity powers lighting, machinery, tools and security systems. In many cases — especially on new sites, in remote locations or during temporary weather events — access to a permanent supply is not an option. That is where temporary power solutions come in.
Selecting the correct type of temporary power system can significantly impact a project’s budget, timeline and environmental footprint. Here is why temporary power is essential for job sites and five of the most common options.
Why Job Sites Need Temporary Power
Temporary power is helpful for job sites that lack permanent electrical infrastructure. Whether launching a new construction project, hosting an outdoor event or managing emergency repairs, access to reliable, short-term electricity is critical for keeping operations safe, efficient and on schedule.
Temporary power enables the operation of tools, lighting, security and communication equipment. Once team members complete the job, they should remove the power source for everyone’s safety.
1. Portable Generators
Portable generators are versatile and easy to transport. They are popular for sites needing flexible, immediate power. They are typically compact, easy to transport and can move as the project demands. These generators usually run on gasoline or diesel and come in various sizes — making them suitable for powering tools, lights and small equipment.
Portable generators can be noisy and disruptive in residential or noise-sensitive sites, and their relatively high fuel consumption may also lead to higher operating costs. However, their overall affordability and accessibility are key advantages. They also do not require a fixed installation so they can be set up quickly without specialized equipment or permits.
2. Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems are increasingly popular as a clean and renewable source for job sites. These systems use photovoltaic panels to convert sunlight into electricity, storing power in batteries when the sun is not shining. Solar power offers a quiet, emission-free alternative, reducing environmental footprint and fuel costs.
The performance of these systems is based on the weather and daylight availability, so it may not provide consistent power in cloudy or shaded areas. Battery capacity and charging speed also limit power availability during peak demands. However, solar systems have a low operating cost after installation, as sunlight is free and maintenance needs are minimal. They can power lighting, communication devices and small tools.
3. Natural Gas Generators
Natural gas generators offer a cleaner-burning alternative that is ideal for sites prioritizing reduced emissions and longer run times. These generators run on compressed natural gas or liquefied natural gas to provide power for heavy equipment, lighting and mobile office units.
These generators require a fixed fuel supply and professional installation. The upfront costs can be higher — especially if infrastructure changes are needed to support fuel delivery. However, natural gas generators emit fewer pollutants than diesel and gasoline engines, making them a better choice for projects with strict air quality regulations. They are also quieter than diesel generators, resulting in fewer disruptions on-site.
4. Diesel Generators
Diesel generators provide robust, reliable power for demanding sites needing continuous high output. Because of their efficiency and durability under heavy loads, they are widely used in construction, mining and large-scale industrial projects. Diesel generators can effectively power heavy machinery, lighting systems and office trailers.
Diesel generators can be bulky and less portable. They often require a dedicated setup space and generate noise and emissions, which can be problematic on sites with strict environmental regulations or residential proximity. To their credit, they offer fuel efficiency and longer run times. Given its low volatility, the fuel is also safe to store and handle.
5. Gasoline Generators
Gasoline generators cater to smaller projects or emergency backup power. They are generally lighter and more portable than diesel models, making them easier to transport and store. They are well-suited to power tools, lighting and small equipment for short periods.
They are typically less fuel-efficient and their fuel tends to be more volatile, requiring careful storage and handling to reduce safety risks. They also require regular oil changes and produce more emissions and noise. Gasoline generators are more suitable for occasional or light-duty use. It is a cost-effective choice for smaller jobs needing portable, short-term power.
The Right Fit Powers Everything
Choosing the right temporary power solution is about aligning energy needs with safety, efficiency, budget and environmental goals. Each option has its strengths. Portable generators offer quick flexibility.
Diesel and gasoline generators deliver reliable muscle, solar systems provide eco-friendly benefits, and natural gas strikes a balance between performance and cleaner emissions. A thoughtful approach ensures a power source keeps lights on and projects on track.